Scenario: You have several servers around the world publishing a website or an application that is accessed by users coming from different countries and geographies. You want to be able to decide which server(s) users will reach based on their country/countries of origin, and you want to handle “fallback” scenarios in case one or more servers are not available. GSLB.me georouting allows the creation of an unrestricted number of “routing rules” to achieve flexible, granular and precise DNS balancing and traffic distribution. Georouting rules can be based on: country of origin of the requesting DNS client region of origin of the requesting DNS client ASN (Autonomous System Number) of origin… Read More
Continue ReadingEnabling DNSSEC
Scenario: You need to enable the “Domain Name System Security Extensions” for one authoritative DNS zone you previously configured (please see the “Create an authoritative DNS zone” howto). How to configure DNSSEC: Log on to GSLB.me using your credentials From the main interface dashboard, click on the authoritative zone you want to enable DNSSEC for The zone configuration dashboard is then displayed. By default DNSSEC is disabled: click on the “Enabled” switch button to turn it on: After turning on the “Enabled” flag, a warning is displayed to remind you that you will have to send the DS record to your registrar, in order to establish the chain… Read More
Continue ReadingConfiguring and using passive checks
Scenario: You need to set up your smart DNS configuration so that the DNS resolution algorithm is driven by externally-fed performance/availability indicators, also known as metrics. In the following configuration example we will assume: the FQDN that will be resolved by clients worldwide is mytest.gslb.eu. This is your website/application host name. you have two servers (targets) that run contents for mytest.gslb.eu: 1 server with IP address 8.8.8.8 1 server with IP address 8.8.4.4 each server is considered available if its CPU load average is < 60% (this is handled by a passive check through metrics pushed to GSLB.me) How to configure it: Log on to GSLB.me using your… Read More
Continue ReadingImporting authoritative zones
Scenario: You want to perform a DNS migration from your current DNS infrastructure (either owned or hosted by a third party) to GSLB.me, and you want to leverage automatic import of your already existing zones. Import must not require manual configuration and must be based on standard DNS zone transfer from your existing authoritative DNS. How to configure it: Log on to GSLB.me using your credentials or register if you still don’t have an account The authoritative zones import dashboard can be accessed either by right-clicking on “Customer zones” on the left panel or on the “DNS zones import” icon in the main screen section. … Read More
Continue ReadingUsing Reporting and Data Intelligence
Scenario: You need to keep track and analyze DNS requests and responses for one of your running geohosts by configuring and customizing graphical reports. How to configure it: Log on to GSLB.me using your credentials or register if you still don’t have an account: To create a new graph from the main screen you can either right-click on the geohost name and select “Reporting engine“: Or you can select the “Geohost reporting engine” from the main panel: After clicking the “Geohost reporting engine” icon you can select the geohost you want to define graphs for using the dropdown menu: Accessing the “Geohost reporting engine” brings you… Read More
Continue ReadingCreate an authoritative DNS zone
Scenario: You want to use GSLB.me as the authoritative DNS for your domain “mydomain.com“. mydomain.com can be a new domain you’re about to register, or it can be an already existing domain. What you get: flexible IPv4 and IPv6 support support for A, AAAA, ALIAS, CAA, CERT, CNAME, LOC, MX, NS, RP, SOA, SPF, SRV, SSHFP, TXT records dynamic DNS support for as many FQDNs as you need configurable TTL for all records (subscribers only) support for wildcard records works with all Internet top level domains easy migration from your legacy DNS provider fast and advanced web user interface seamless configuration, no need to manage master and slave… Read More
Continue ReadingSet up Dynamic DNS
Scenario: You want to use GSLB.me as the authoritative DNS for your domain “mydomain.com“. mydomain.com can be a new domain you’re about to register, or it can be an already existing domain. Once done, you want to run “www.mydomain.com” from your webserver which sits on an Internet connection with a dynamic IP. How to configure it: Log on to GSLB.me using your credentials or register if you still don’t have an account Create a new “customer zone”: this is the domain name you want to handle using GSLB.me as your authoritative DNS. You can create a customer zone for a domain name you already own (in this case… Read More
Continue ReadingGeographical Proximity
Scenario: You have at least two datacenters running the same application and both datacenters are simultaneously active (business continuity) Your application is mapped on a well-defined hostname (ie. www.myapplication.com) On the first datacenter www.myapplication.com is running on IP a.b.c.d. One the second datacenter www.myapplication.com is running on IP x.y.z.t You need your clients traffic to be sent to the geographically closest datacenter through geographical proximity Solution: Use GSLB.me in geographical balancing mode Define one geohost that will be pointed by www.myapplication.com via a DNS CNAME record Create two targets, one for each datacenter Assign the relevant checks to each target Configure the CNAME record on the primary DNS… Read More
Continue Reading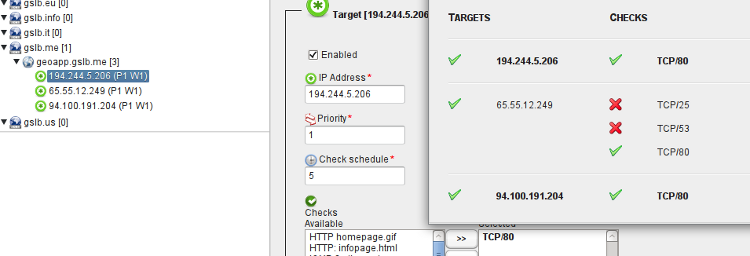
Active-Standby between two datacenters
Scenario: You have at least two datacenters running the same application. The primary datacenter is always active. In case of failure/disaster the secondary/backup datacenter must kick in taking control and providing access to your application (disaster recovery) Your application is mapped on a well-defined hostname (ie. www.myapplication.com) On the primary datacenter www.myapplication.com is running on IP a.b.c.d. One the secondary/backup datacenter www.myapplication.com is running on IP x.y.z.t You need your clients traffic to be sent to the primary datacenter and, only in case of unavailability, be transparently sent to the secondary/backup datacenter Solution: Use GSLB.me in priority balancing mode Define one geohost that will be pointed by www.myapplication.com… Read More
Continue ReadingLoad balancing between two datacenters
Scenario: You have at least two datacenters running the same application and both datacenters are simultaneously active (business continuity) Your application is mapped on a well-defined hostname (ie. www.myapplication.com) On the first datacenter www.myapplication.com is running on IP a.b.c.d. One the second datacenter www.myapplication.com is running on IP x.y.z.t You need your clients traffic to be equally split between the two datacenters Solution: Use GSLB.me in round robin balancing mode Define one geohost that will be pointed by www.myapplication.com via a DNS CNAME record Create two targets, one for each datacenter Assign the relevant checks to each target Configure the CNAME record on the primary DNS server that… Read More
Continue Reading